Automate Your Content. Amplify Your Reach.
Say goodbye to manual updates. Our intelligent syndication network connects brands and retailers effortlessly, delivering content that converts.
Trusted by the World’s Leading Brands & Retailers












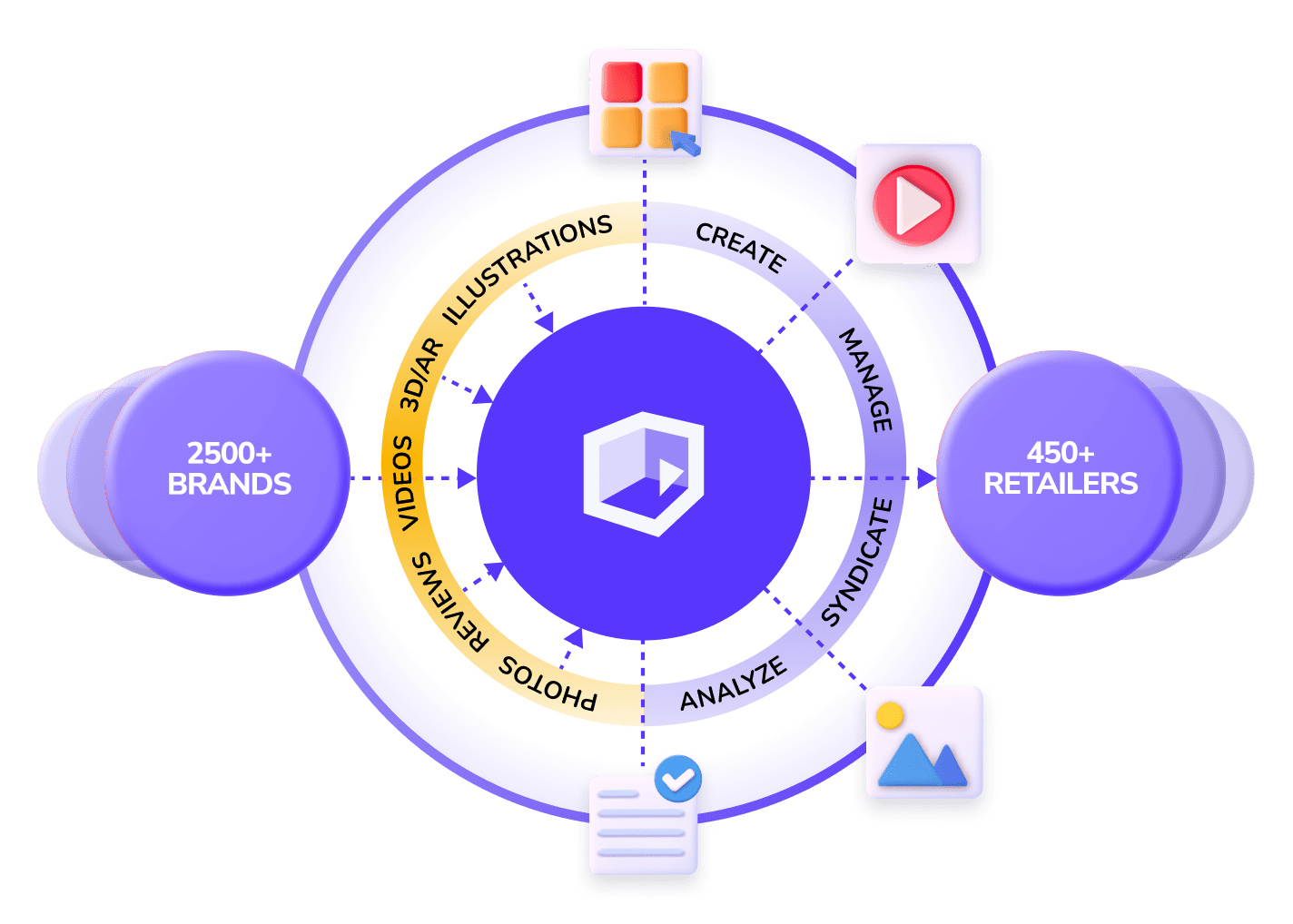
A Full Product Content Ecosystem
From managing assets to creating engaging content, get solutions for the entire content lifecycle.
Content Syndication Network
A global network helping brands publish and retailers curate high-quality PDP content – automatically.
Join the NetworkDigital Asset Management
Organise, store, and deliver content at scale, with features like a dynamic creative editor and reliable image CDN.
Book DemoContent Creation Services
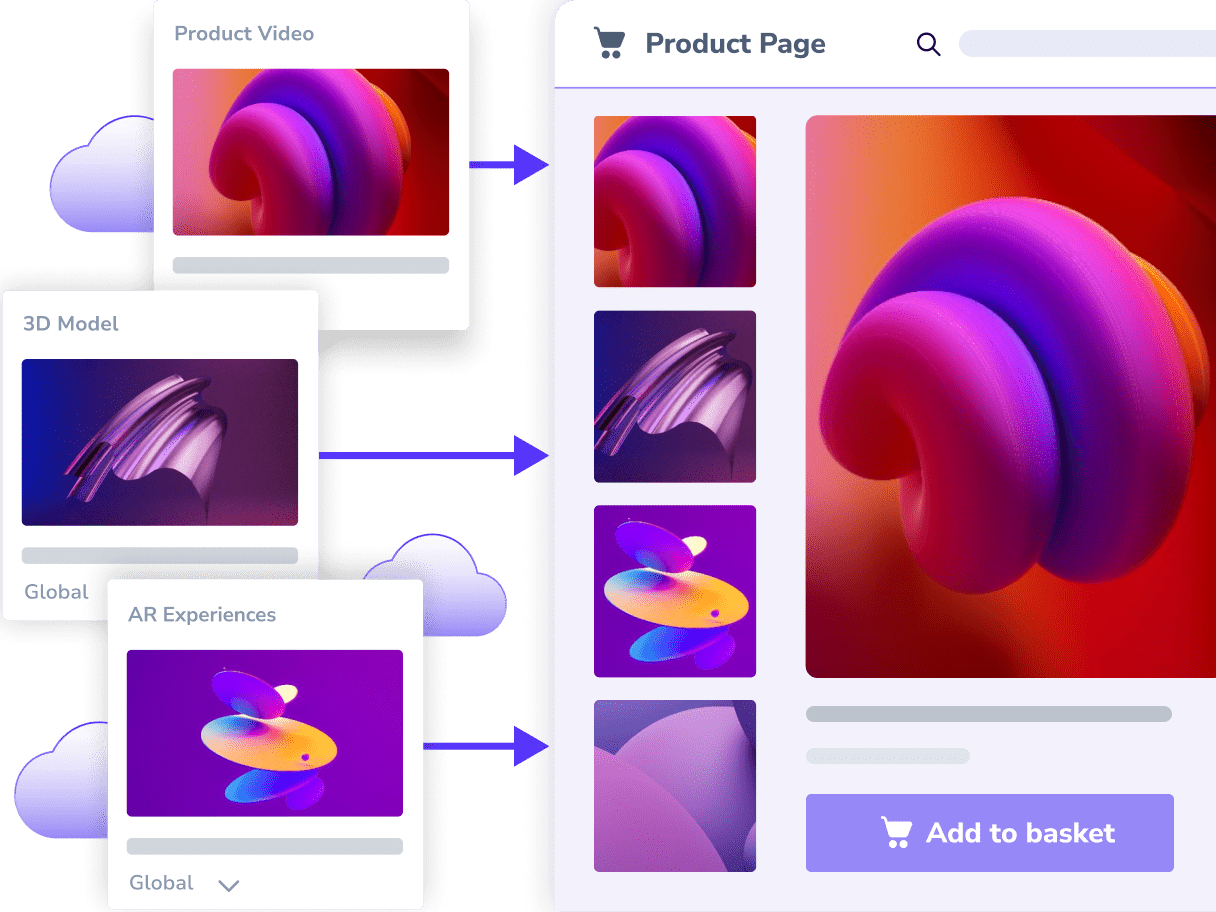
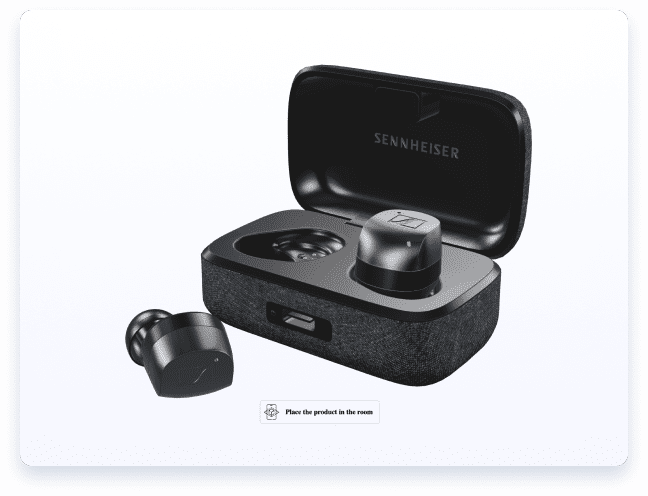
Bring products to life with review videos, animated clips, and immersive 3D/AR to boost engagement and sales.
Get QuoteEAA Compliance Solutions
Effortlessly meet accessibility standards across content types and create inclusive experiences for every customer.
Comply TodayWhether you're a brand looking to scale content distribution or a retailer optimising the shopper experience, our ecosystem is built to grow your e-commerce success.
Discover Our Full EcosystemThe Cure for Chaotic E-Commerce Content
Automate your entire content workflow! Our syndication network automates product updates, keeps listings consistent, and ensures you reach the right audience with the right content on every PDP.
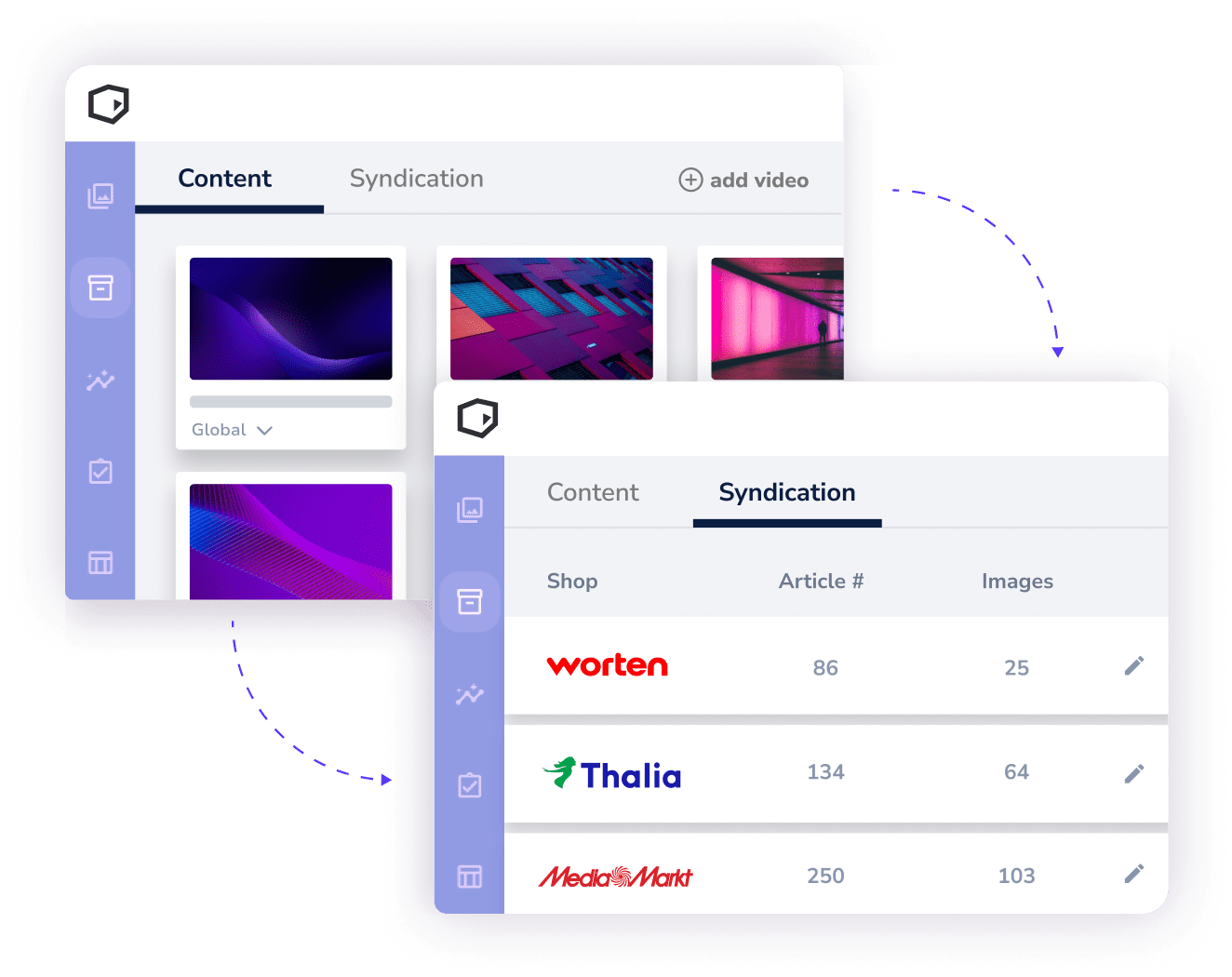
Automated, One-Time Uploads for Brands
Distribute product content seamlessly across all retail partners, saving time and ensuring accuracy.
Instant, High-Quality Updates for Retailers
Retailers receive up-to-date, optimised content automatically, enhancing the customer experience and driving sales.
Everything You Need to Reach Your Target Audience, All in One Place
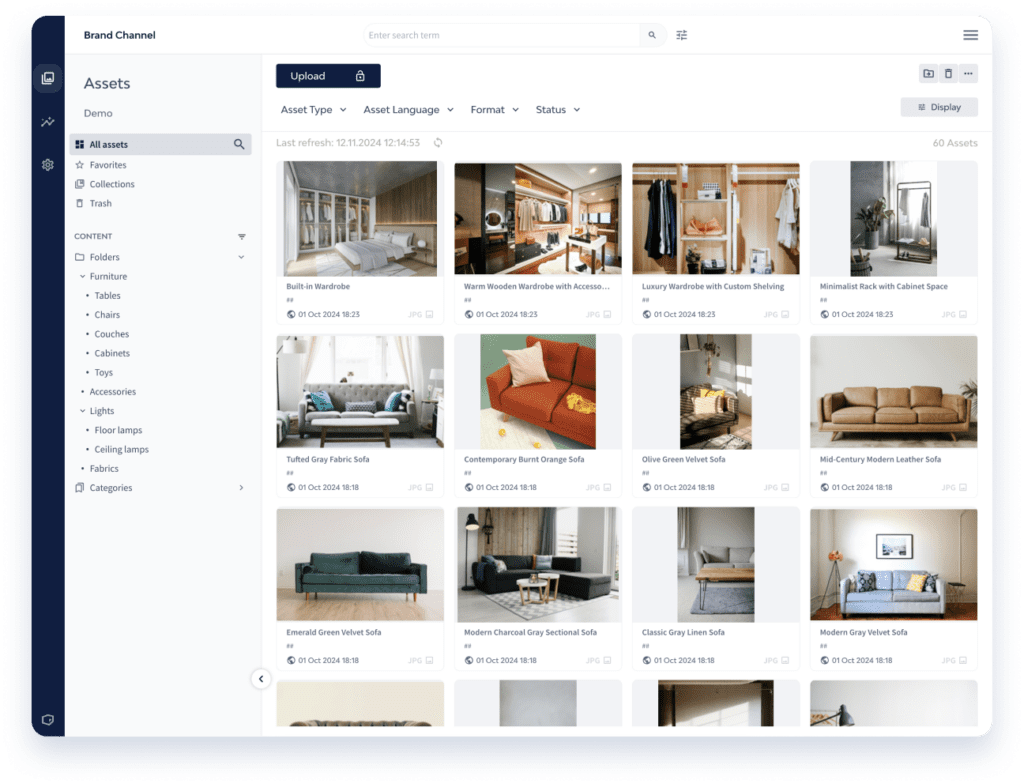
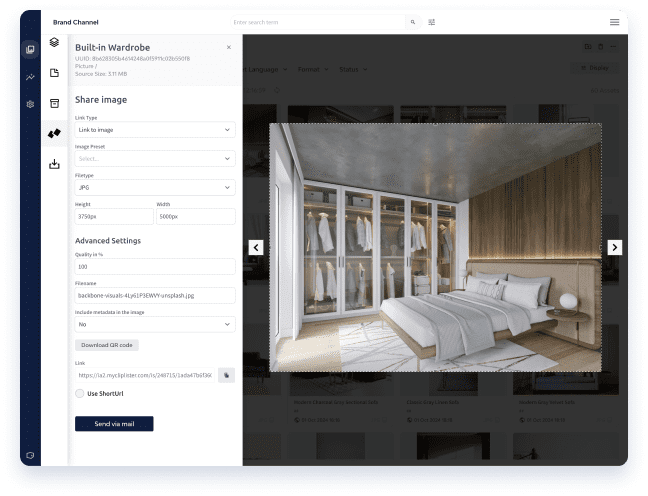
Comprehensive E-Commerce DAM Solutions

Content Creation Services



What Our Customers Say
Read what our customers have to say about DemoUp Cliplister








